The liver plays an important role in the body. In fact, it performs more than 500 different functions.
One of the most important is detoxification. The liver removes toxins like alcohol from the bloodstream. Plus, it plays a role in immunology, metabolism and red cell blood production.
However, as we age, the liver can start to function inefficiently. Infection, obesity and autoimmune disease can also contribute to reduced liver function. The result? Toxins begin to build up, hormone imbalance, and an increased risk for infection.
So, how can we improve and maintain healthy liver function? A method that’s currently under research is using red light therapy for liver health.
Although the research is still in the early stages, red light therapy shows promise. Recent research suggests RLT may increase liver cell production, treat fatty liver disease, and potentially reduce cirrhosis symptoms.
So, is red light therapy for liver health a viable option?
Let’s explore the exciting research into red light therapy for liver detox and the key mechanisms at play.
What Role Does the Liver Play in Health?
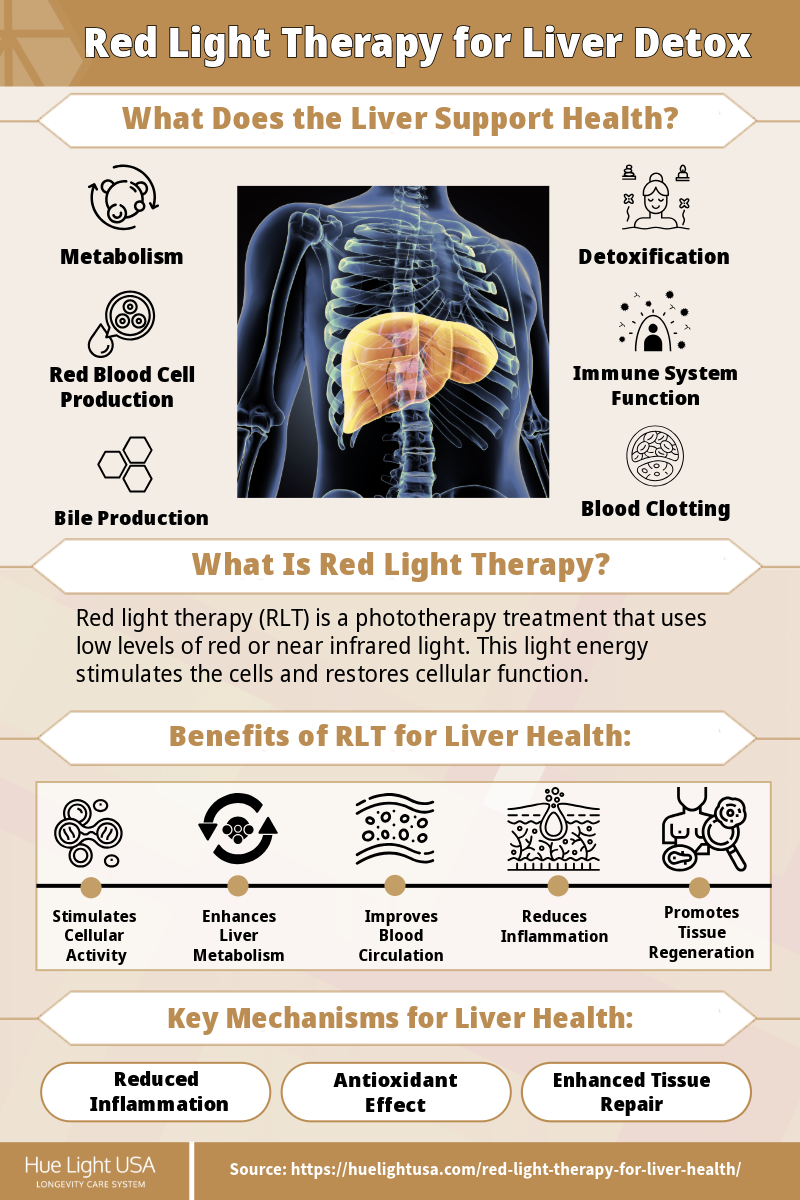
The liver is a large, complex organ that plays a vital role in keeping the body healthy. It’s often referred to as the body’s “chemical factor,” because it performs more than 500 different functions. They include:
- Detoxification: The liver removes toxins, such as alcohol, drugs, and pollutants, from the bloodstream.
- Metabolism: The liver breaks down nutrients into forms that the body can use for energy. It also stores excess glucose as glycogen, which can be released into the bloodstream when needed. Red light therapy may also support gut health, another benefit for metabolism.
- Bile production: Bile is a fluid that helps break down fats in the small intestine.
- Blood clotting: The liver produces proteins that are essential for blood clotting.
- Red blood cell production: The liver helps to produce red blood cells in the fetus and in some adults with certain conditions.
- Immune system function: The liver produces immune factors and removes bacteria from the bloodstream.
Because the liver is so complex, it’s difficult to pinpoint one single function that’s “most important.” However, detoxification is arguably the most crucial. As a detoxifier, the liver filters out harmful substances and prevents them from damaging other organs.
Therefore, for long-term health, we must support liver function. And there’s some surprising ways that red light therapy can help.
Mechanisms of Red Light Therapy for Liver Detox
What Is Red Light Therapy? What Are Its Benefits for Liver Health?
Red light therapy is a form of photobiomodulation. They aren’t the same thing. Photobiomodulation refers to using light energy to treat the body, whereas RLT refers to photobiomodulation using only near infrared and red light wavelengths.
Improving Cell Energy Production
Generally, research suggestions that RLT activates the production of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), our cell’s main energy source.
This increase may enhance cellular function within the liver, and several animal studies have found RLT stimulates the production of liver cells and enzymes. Ultimately, this enhanced function may promote better detoxification and metabolic processes.
Additional Key Mechanisms for Liver Health
However, there are other mechanisms at play. Some other mechanisms that may benefit liver function include:
- Reduced inflammation: Chronic inflammation is a major contributor to liver damage. Red light therapy’s anti-inflammatory properties [1] may help reduce inflammation in the liver, creating a more favorable environment for healing and regeneration.
- Antioxidant effect: Some research suggests RLT may enhance the body’s natural antioxidant defenses. Specifically for liver conditions, red light therapy may boost the liver’s ability to produce antioxidants. In fact, an 2009 animal study [2] concluded that RLT helped to reduce acute hepatic oxidative stress by enhancing the liver’s antioxidant defense system.
- Enhanced tissue repair: Red light therapy is believed to stimulate cell proliferation and migration, which could aid in the repair of damaged liver tissue. In addition, RLT has been shown to increase fibroblast proliferation, stimulate angiogenesis, which also signals its tissue-repairing properties. [3]
Ultimately, our understanding of how photobiomodulation works is evolving. However, ongoing research continues to explore them to help us better understand the mechanisms that support well-being.
Does It Work? Exploring RLT for Liver Clinical Research
Red light therapy and photobiomodulation are relatively new medical interventions. In fact, it was discovered by accident in 1967. However, in the last two decades research into this subject has exploded.
Currently, studies exploring red light therapy for liver health are limited, with the existing literature involving animal populations and small randomized clinical trials.
Here’s a look at some of the most promising research:
RLT for Fatty Liver
Fatty liver occurs when excess fat cells proliferate in the liver. It can be caused by alcohol abuse, obesity and other factors. And red light therapy may help improve outcomes for fatty liver sufferers.
A 2021 study [4] compared 60 patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). The first was treated with the Mediterranean diet, while the other tried the same diet along with red light therapy. Following the study, both groups experienced improvements in liver enzymes and blood lipid profiles.
However, the group that received the Mediterranean diet and red light therapy had markedly better results. Researchers concluded that RLT might be a viable treatment approach to improve liver function.
Liver Cell Production
Numerous studies have found red light therapy has a positive impact on tissue regeneration and cell vitality. Studies on its impact to liver cells is limited; however, several small in vitro and animal studies have found that red light therapy stimulates liver cell proliferation.
A 2018 study [5] published in the journal Hepatol Research found that red light irradiation increased the proliferation of liver cells through the ROS/pERK1/2 pathway. Ultimately, researchers concluded this could be a useful method for increasing the number of liver cells available for transplantation.
Similarly, a 2013 study [6] published in Lasers in Medical Science found that RLT improved liver regeneration after a partial hepatectomy in rats. Researchers found an increase of hepatocyte growth factor in important signaling pathways for liver regeneration.
RLT for Oxidative Stress in the Liver
Hepatic oxidative stress is believed to be a factor in liver disease. [7] And red light therapy may help to reverse oxidative stress by enhancing our antioxidant defense system.
A 2009 study [8] explored the impact of red light therapy (specifically near infrared light) on oxidative stress in the liver. Researchers found that RLT showed promise for treating oxidative stress in acutely diabetic rates, but not in chronically diabetic rats. The researchers concluded that RLT may, in part, reduce hepatic oxidative stress.
Light Therapy and Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis is the progressive scarring and distortion of healthy liver tissue. It’s caused primarily by alcohol abuse and infections.
A study published in the journal Photochemistry and Photobiology found that red light therapy helped improve liver function [9] and reduce inflammation in an animal population with induced liver cirrhosis.
Ultimately, this is very preliminary research and shouldn’t be taken as definitive evidence. However, there’s a clear implication that red light therapy affects liver function and health. More research is needed to understand how and why this happens.
Wrapping Up
The liver is one of the body’s most important organs, and there are many ways you can support it. A healthy, balanced diet is, first and foremost, an important tool for maintaining liver health.
Second, focus on lifestyle factors like maintaining a healthy weight, getting enough rest and avoiding environmental toxins will also support liver health too. However, if you’re looking for additional strategies, abdominal red light therapy may offer benefits, along with supplementation. Ultimately, always consult a healthcare professional regarding your decisions.
Hue Light USA offers a variety of state-of-the-art red light therapy devices for home or commercial use. Contact us today to learn more.
References
1. Hamblin MR.Mechanisms and applications of the anti-inflammatory effects of photobiomodulation. AIMS Biophys. 2017;4(3):337-361.
2. Lim J, Ali ZM, Sanders RA, Snyder AC, Eells JT, Henshel DS, Watkins JB 3rd. Effects of low-level light therapy on hepatic antioxidant defense in acute and chronic diabetic rats. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2009 Jan-Feb;23(1):1-8.
3. Chaves ME, Araújo AR, Piancastelli AC, Pinotti M. Effects of low-power light therapy on wound healing: LASER x LED. An Bras Dermatol. 2014 Jul-Aug;89(4):616-23.
4. Nagy EN, Ibrahim FM, Jouda AA, Elsayed MM. The Effect of Laser Therapy Along With Mediterranean Diet Versus Mediterranean Diet Only on Older Adults With Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Randomized Clinical Trial. J Lasers Med Sci. 2021 Jul 24;12:e39.
5. Feng R, Morine Y, Ikemoto T, Imura S, Iwahashi S, Saito Y, Shimada M. Photobiomodulation with red light-emitting diodes accelerates hepatocyte proliferation through reactive oxygen species/extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway. Hepatol Res. 2018 Oct;48(11):926-936.
6. Araújo TG, de Oliveira AG, Tobar N, Saad MJ, Moreira LR, Reis ER, Nicola EM, de Jorge GL, dos Tártaro RR, Boin IF, Teixeira AR. Liver regeneration following partial hepatectomy is improved by enhancing the HGF/Met axis and Akt and Erk pathways after low-power laser irradiation in rats. Lasers Med Sci. 2013 Nov;28(6):1511-7
7. Sadasivam N, Kim YJ, Radhakrishnan K, Kim DK. Oxidative Stress, Genomic Integrity, and Liver Diseases. Molecules. 2022 May 15;27(10):3159.
8. Lim J, Ali ZM, Sanders RA, Snyder AC, Eells JT, Henshel DS, Watkins JB 3rd. Effects of low-level light therapy on hepatic antioxidant defense in acute and chronic diabetic rats. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2009 Jan-Feb;23(1):1-8.
9. Oliveira-Junior MC, Monteiro AS, Leal-Junior EC, Munin E, Osório RA, Ribeiro W, Vieira RP. Low-level laser therapy ameliorates CCl4-induced liver cirrhosis in rats. Photochem Photobiol. 2013 Jan-Feb;89(1):173-8.